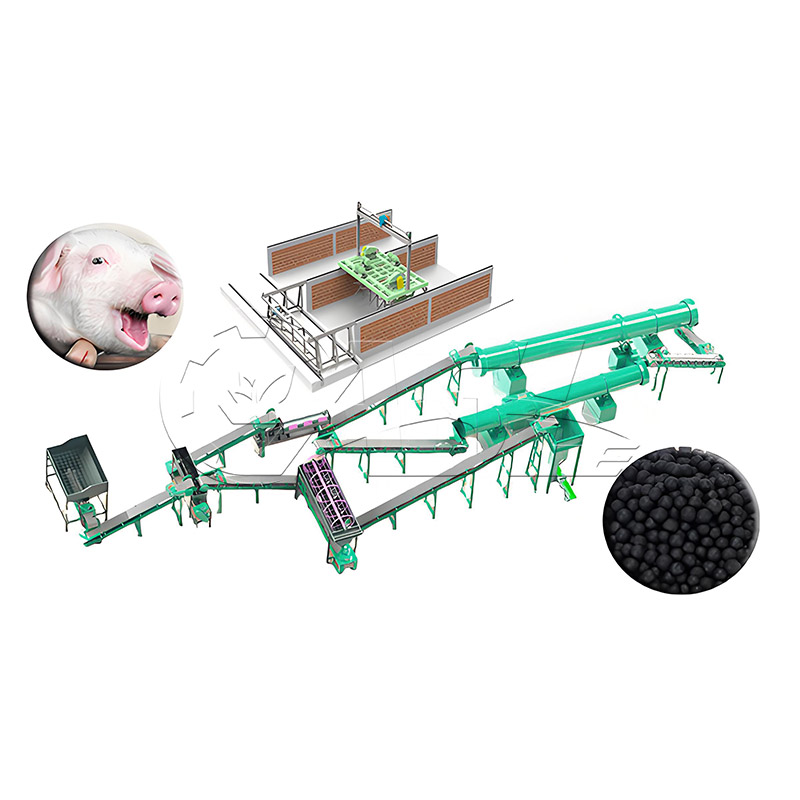
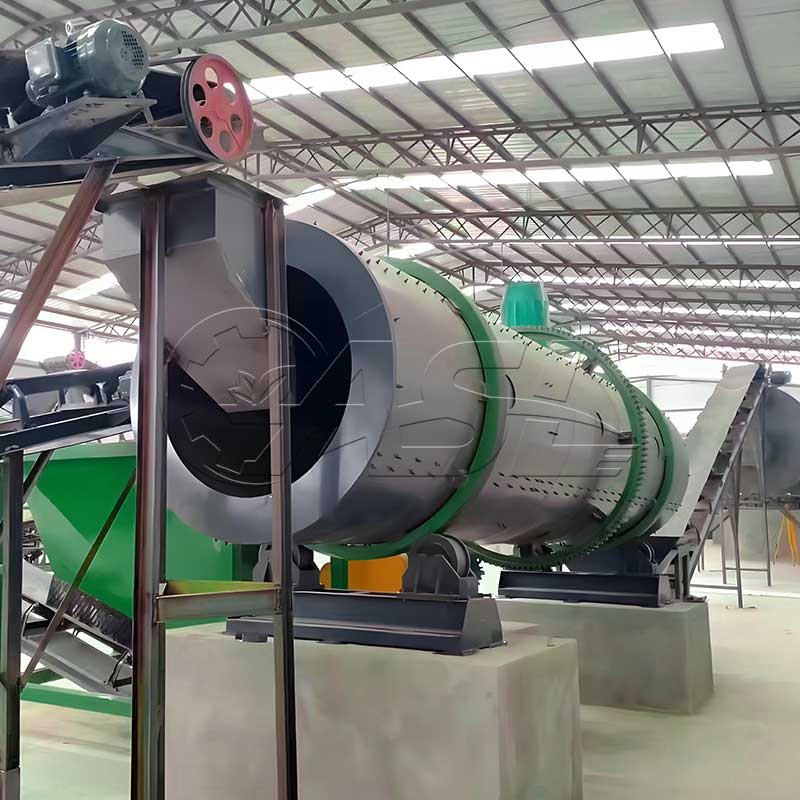
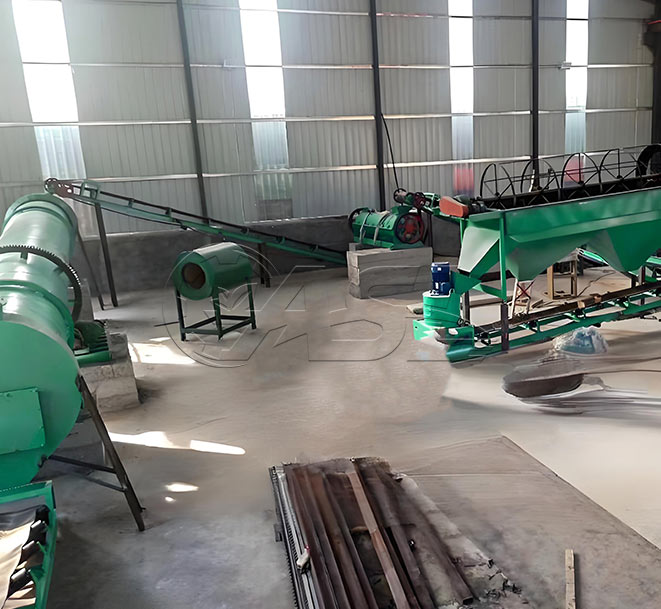
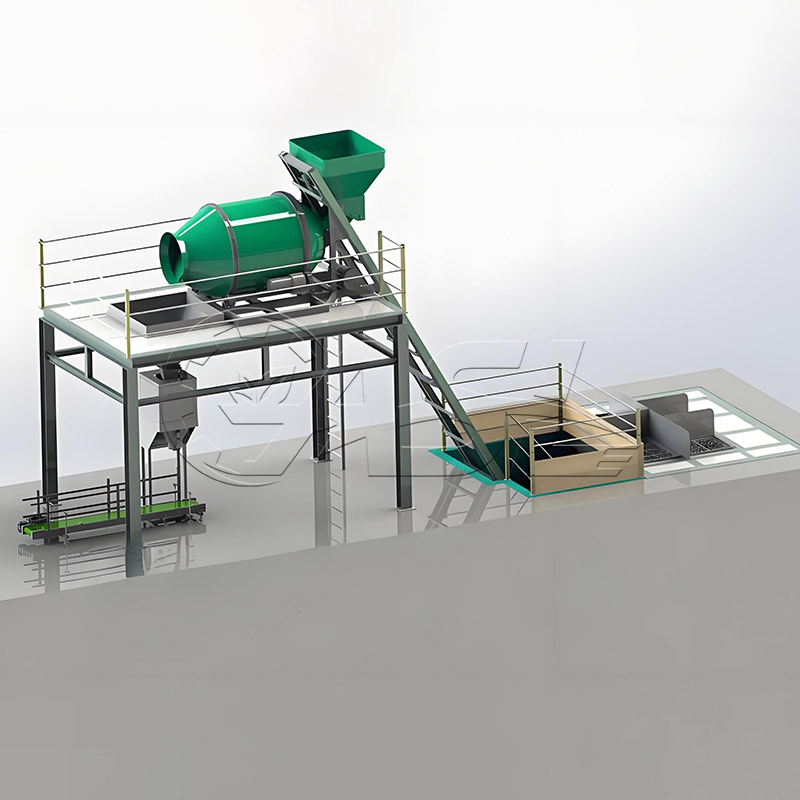
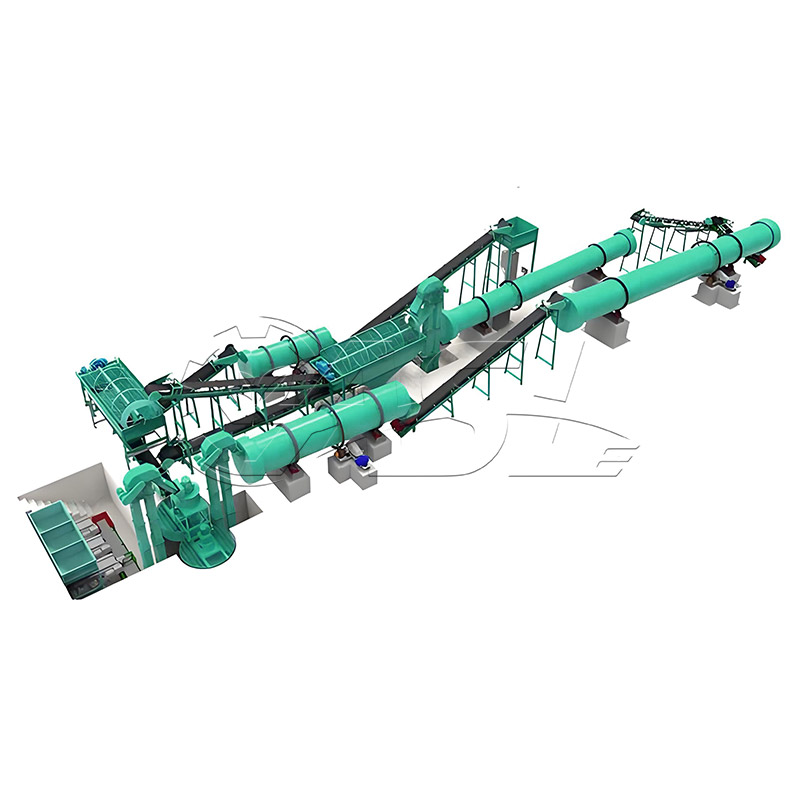
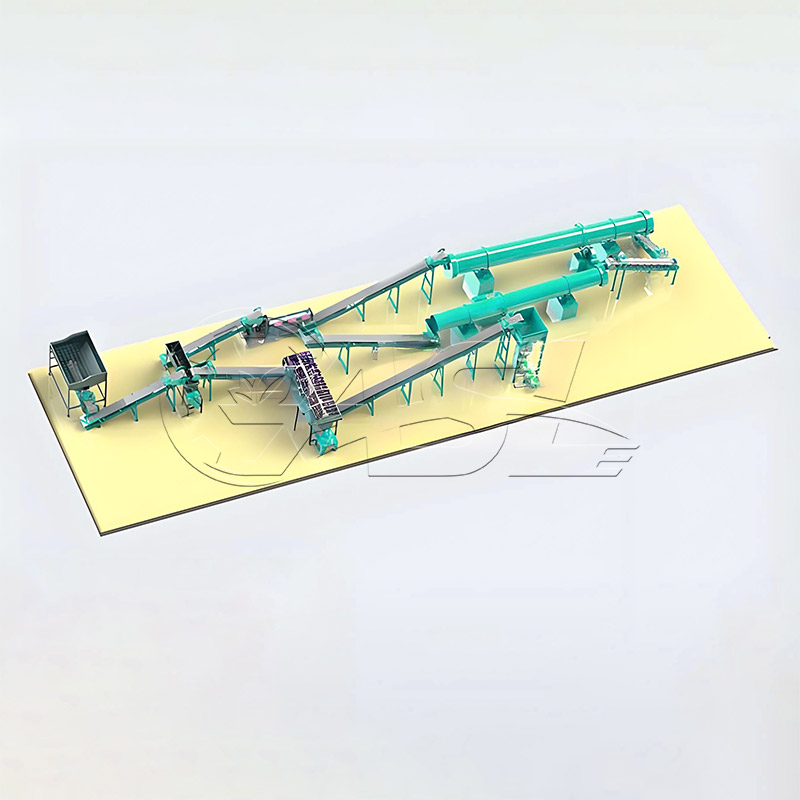
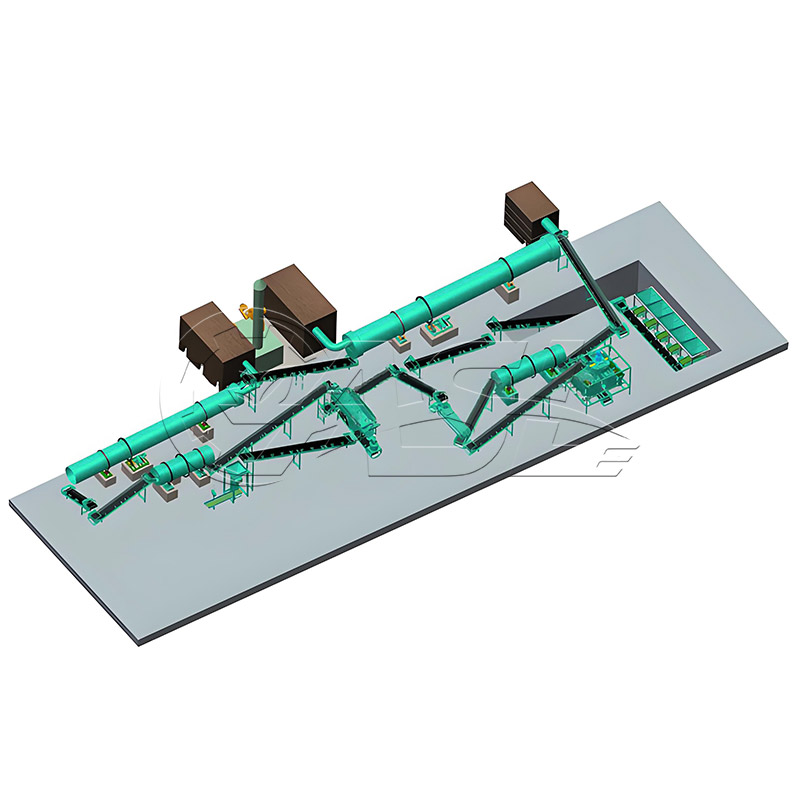
1. What core equipment is required for a pig manure organic fertilizer production line?
Answer: Core equipment includes pretreatment equipment (screening machines, solid-liquid separators to remove impurities and excess water from the manure), fermentation equipment (trough turners and fermentation tanks to mature the manure), further processing equipment (crushers, mixers, and granulators to convert the matured material into granular fertilizer), drying and cooling equipment (drum dryers and coolers to adjust the moisture content of the finished product), and packaging equipment (automatic quantitative packaging machines to package the finished product). Small production lines can simplify some equipment, while large production lines require environmental protection equipment (deodorizers and dust collectors).
2. How long does it take for pig manure to mature? Can the production line operate continuously?
Answer: Natural fermentation takes 15-30 days. Using high-temperature aerobic fermentation tanks can shorten this time to 7-10 days. A fully configured production line can operate continuously. That is, while one batch of material is mature, another batch enters pretreatment. The entire process (pretreatment - fermentation - further processing) can be completed in a single day. Small production lines, due to the limited number of equipment, may require alternate days of production.
3. Are there any moisture content requirements for the pig manure produced during the production line? What should I do if the moisture content is too high?
Answer: During the pretreatment phase, the moisture content of the pig manure should be controlled at 60%-65% (it should form a ball when squeezed by hand and fall apart when dropped to the ground). Excessively high moisture content will result in incomplete fermentation and produce a foul odor. If the moisture content exceeds 70% (such as fresh pig manure), two treatment methods are available: one is to use a solid-liquid separator to separate the excess water, and the other is to add dry auxiliary materials.
4. Does the production process produce foul odors? What environmental treatment measures are required?
Answer: The fermentation stage produces a small amount of odors such as ammonia and hydrogen sulfide. If left untreated, these can affect the surrounding environment. Two types of environmental protection equipment are required: a deodorization device (a biofilter or spray tower, which uses microorganisms or chemical reagents to decompose odors, with a deodorization efficiency of over 90%), and an exhaust gas collection system (which directs exhaust gas from the fermentation workshop into the deodorization device to prevent its spread). In addition, the finished product warehouse must be well ventilated to prevent dust pollution. A pulse dust collector can be installed.
5. What are the requirements for factory site selection? Does it need to be far from residential areas?
Answer: The site must meet three core criteria: First, it must be close to raw material sources, such as large-scale pig farms, to reduce transportation costs. A distance of 10 kilometers or less is recommended. Second, it must be conveniently located near highways to facilitate the transportation of finished products. Third, it must meet environmental protection requirements and be away from sensitive areas such as residential areas, water sources, and schools. The distance is generally 500 meters or more. Furthermore, the site must be flat to facilitate equipment installation and drainage, avoiding low-lying areas prone to flooding.