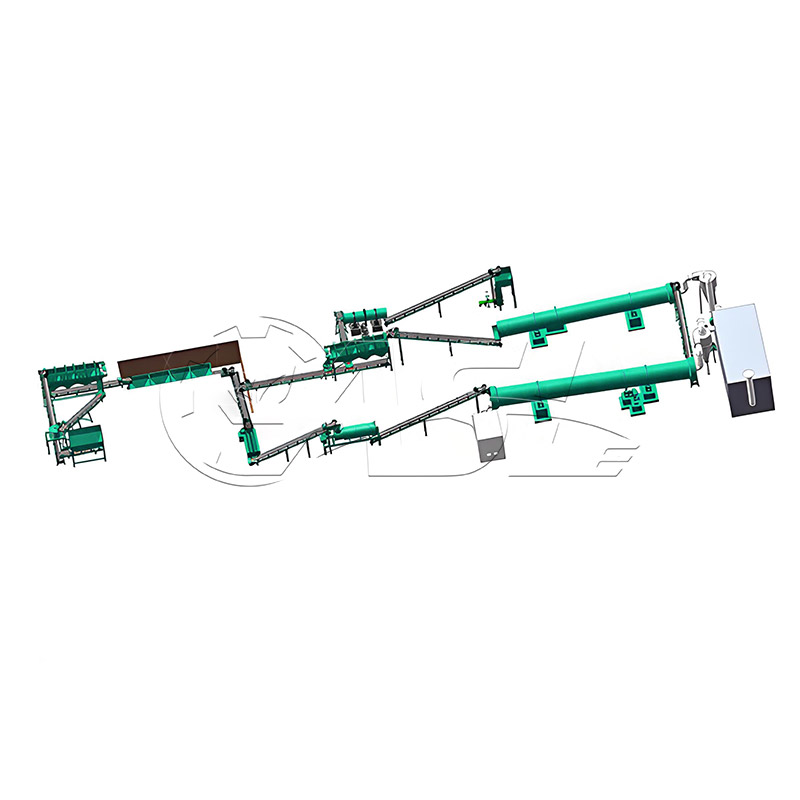
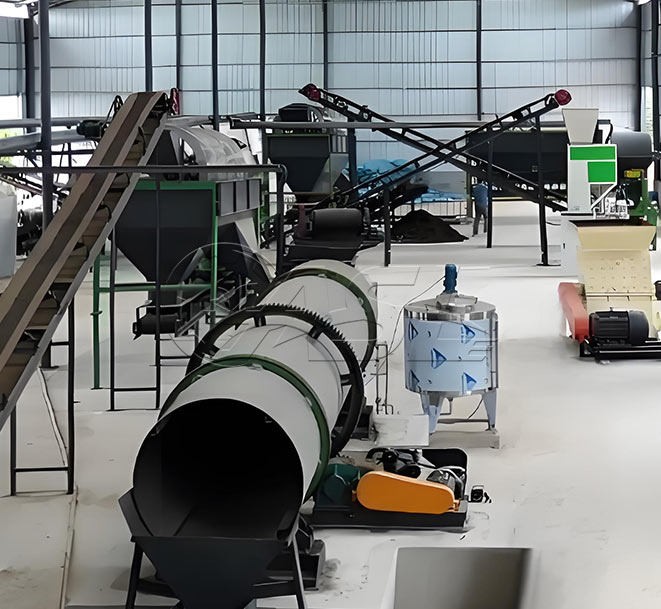
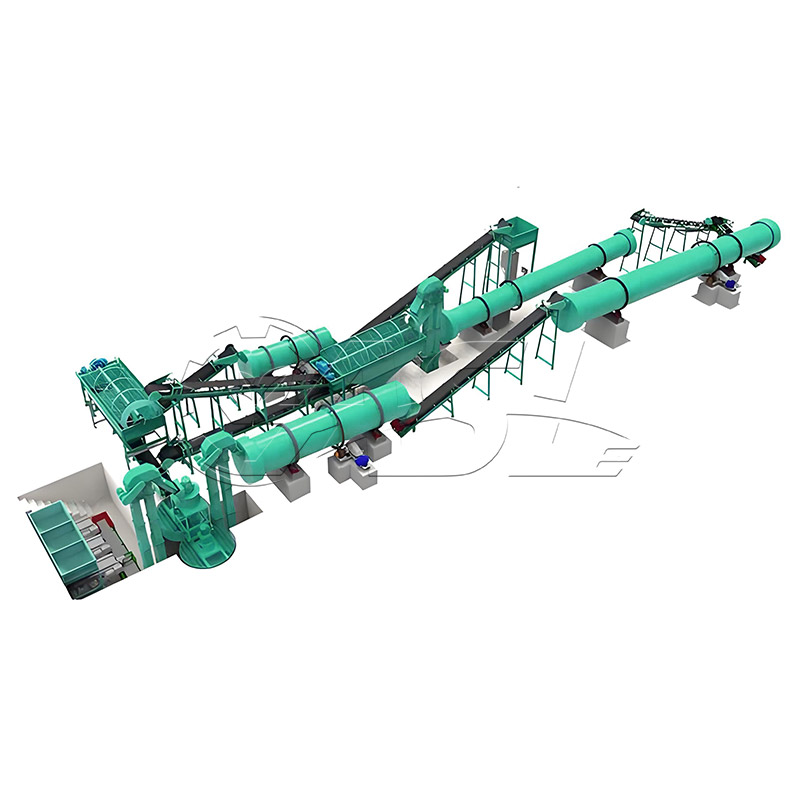
What raw materials can a drum granulation line process? Are there any specific requirements for the raw material properties?
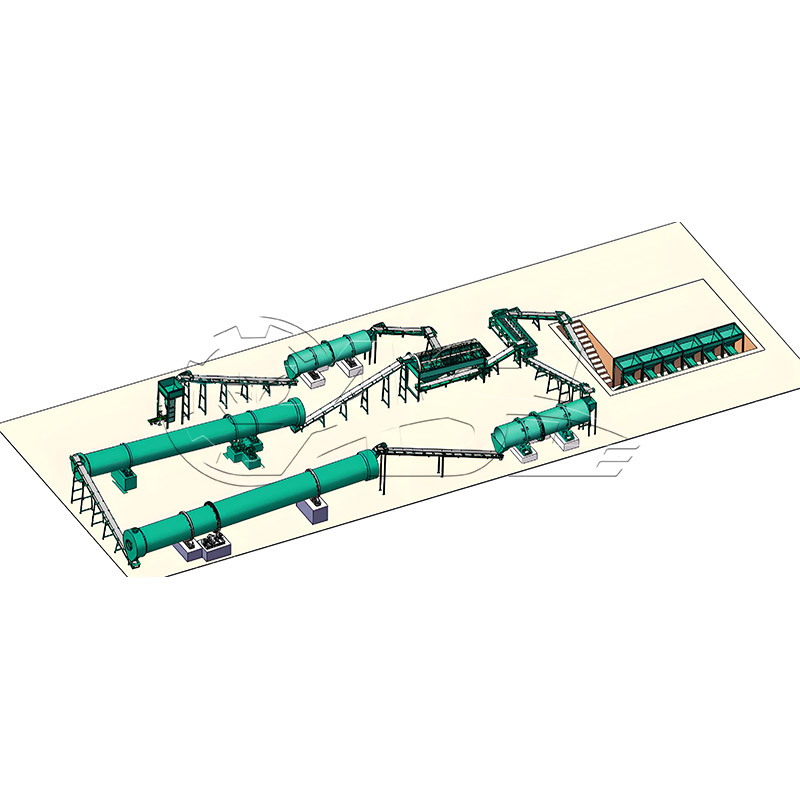
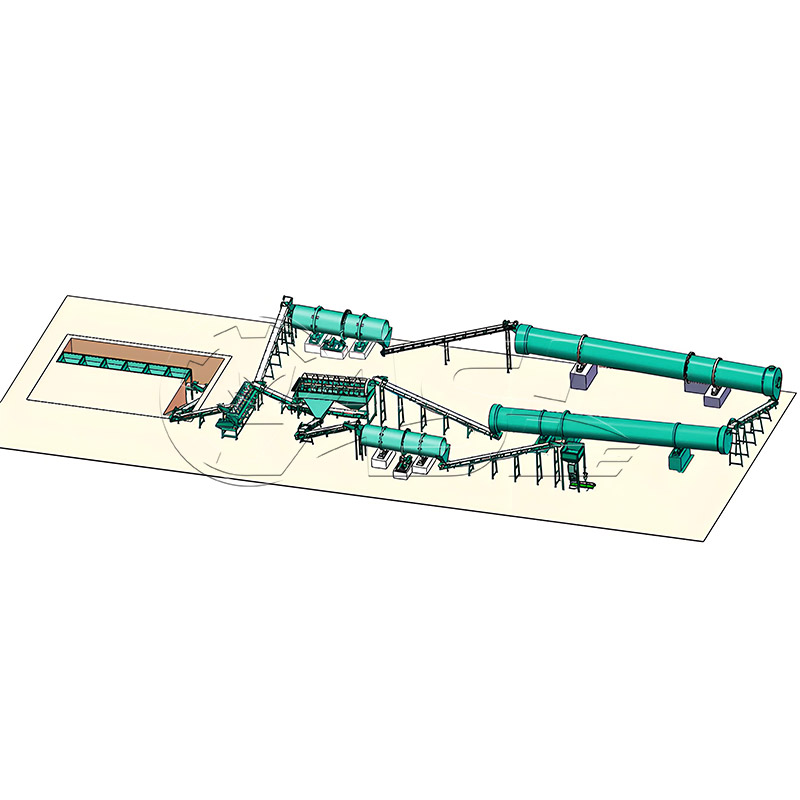
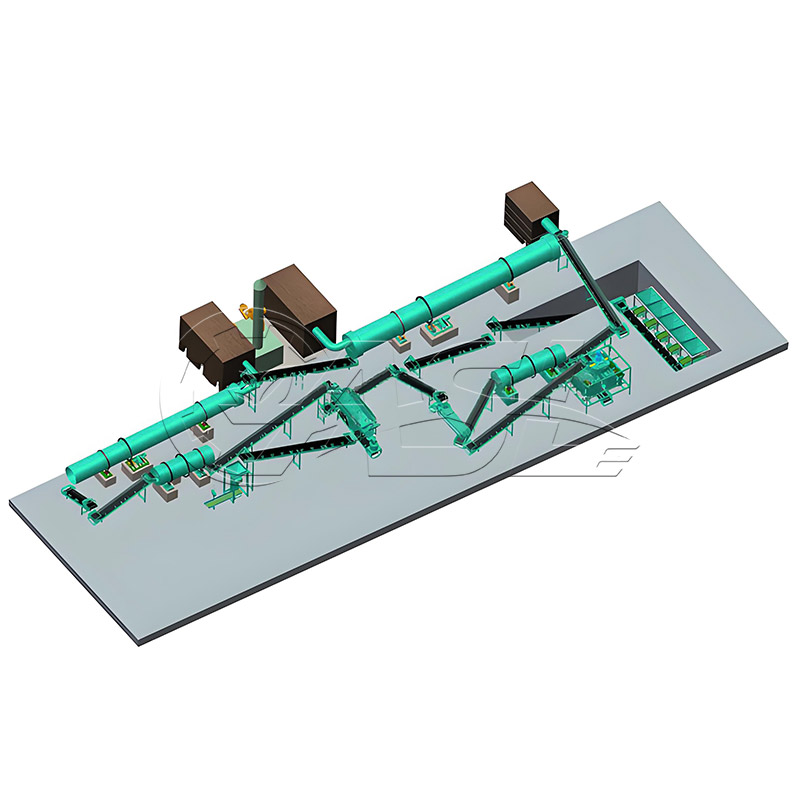
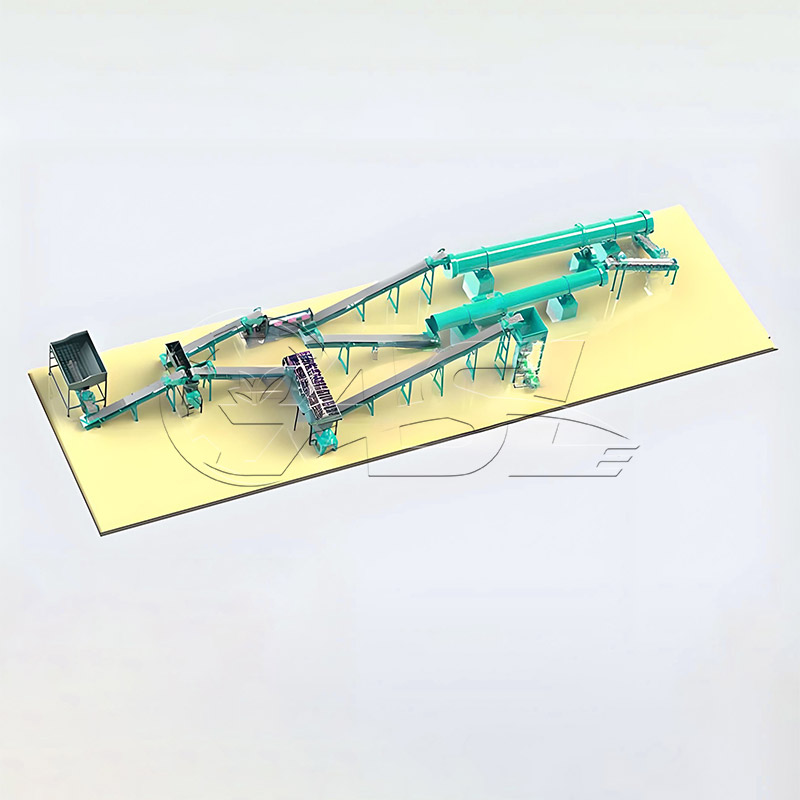
It can process organic raw materials (fermented livestock and poultry manure, straw powder, mushroom residue), inorganic raw materials (urea, diammonium phosphate, potassium chloride, slag), and mixed raw materials (organic-inorganic compound fertilizer raw materials). The raw materials must have uniform particle size and a certain degree of viscosity. Avoid non-sticky materials such as pure sand or pure fiber, as granulation will be difficult.
What are the wearing parts of a drum granulator?
Wearing parts include the drum liner, lifter plate, drive bearings, and seals. Under normal use, the service life of the liner is 8-12 months (for organic materials) or 5-8 months (for inorganic hard materials), the lifter plate is 6-10 months, and the bearings are 1-2 years.
How many workers are needed to operate a drum granulation line? Are specialized technicians required?
A production line with an hourly output of 5-15 tons requires 6-8 people; a production line with an hourly output of 15-30 tons requires 10-12 people. Adding an automated control system can reduce the number of people by 2-3. One professional technician is required, and ordinary workers can begin work after a week of factory training. No professional qualifications are required.
What raw materials are suitable for a rotary drum granulation line? Can it produce organic fertilizer and compound fertilizer?
Rotary drum granulation lines are highly adaptable to various raw materials and are primarily suitable for organic fertilizer, compound fertilizer, biofertilizer, and inorganic fertilizer. When processing organic fertilizer, pretreatment equipment is required to ensure the raw material moisture content is controlled at 30%-45%. When processing compound fertilizer, the binder ratio can be adjusted to accommodate different ratios of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium raw materials.
After the production line is shut down, how can the inner wall of the rotary drum be cleaned to prevent residual material agglomeration?
After shutting down, follow the "three-step cleaning method":
Initial Cleaning: Immediately after shutting down, open the drum inspection door and use a scraper to remove any remaining wet material from the inner wall. The removed wet material can be temporarily stored and returned to production the next time the machine is restarted.
Warm Water Rinse: If the remaining material is viscous, use a high-pressure water jet with 40-50°C warm water to rinse the inner wall, focusing on the gaps between the scrapers and welds.
Drying and Rust Prevention: After rinsing, start the drum and idle for 10-15 minutes to use the residual heat to dry the inner wall. Finally, apply a thin layer of engine oil evenly to the inner wall to prevent rust.